●) Fire alarm
Components required:
Power supplyResistors (1kΩ)
Potentiometer (10KΩ)
Capacitor (10µF, 16V)
BC548 transistor
High resistance thermistor (NTC)
Diode (1N4001)
6V Buzzer
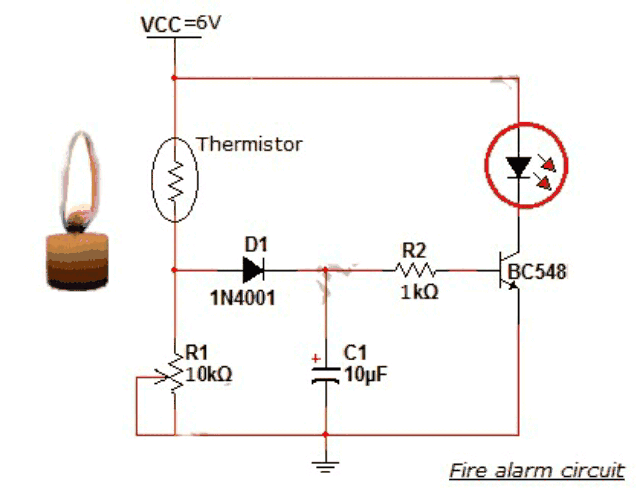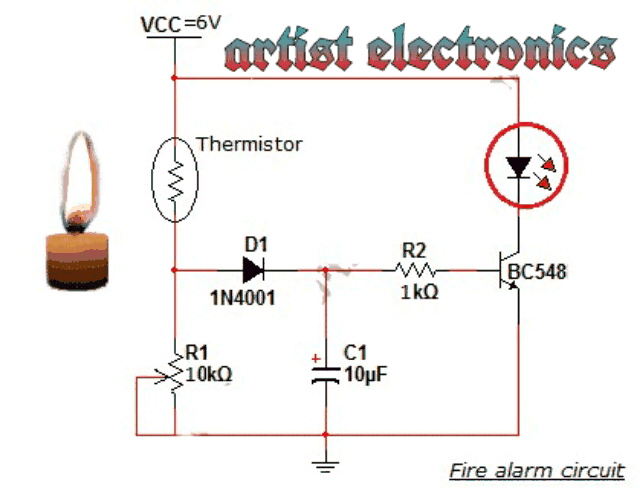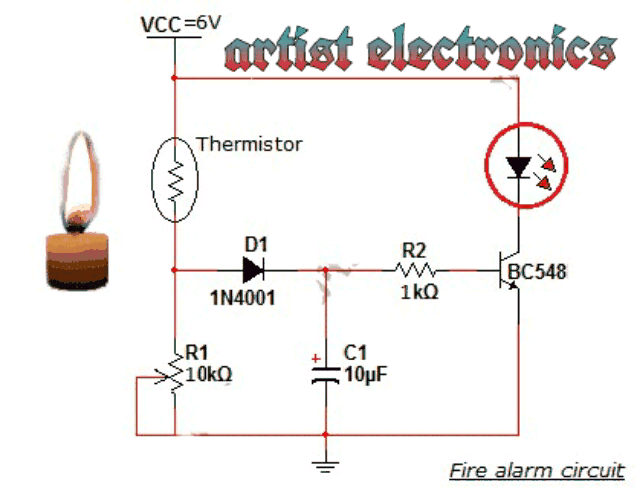
Working of fire alarm circuit
The thermistor and R1 forms a potential divider network which drives the transistor.
The heart of this circuit is a thermistor. Thermistors are low-cost, easily-available temperature sensors widely used for uncomplicated temperature measurements.
Thermistors are temperature sensitive resistors. When temperature increases resistance offered by the thermistor decreases and vice versa. At normal temperature, the resistance of the thermistor is around 10kΩ.
All resistors vary with temperature, but the semiconductor materials used for thermistors are especially sensitive to temperature.
The transistor is turned ON by the voltage drop across the resistor R1.
Consider the temperature of the atmosphere is around 25°C, and then the resistance of thermistor is high so the voltage across the thermistor is also high according to the basic ohm’s law V=IR.
The threshold voltage can be set by varying the potentiometer (R1).
At this situation voltage across resistor R1 is low and it is not sufficient to turn on the transistor.
As temperature rises, the resistance of thermistor decreases so that the drop across the resistor R1 increases which turns ON the transistor.
When the transistor is turned ON, the current from Vcc starts to flow via 6V buzzer which produces a beep sound.
Diode is used for enabling unidirectional conduction and the capacitor removes sudden transients from the thermistor.
Components required:
Power supply
Resistors (1kΩ)
Potentiometer (10KΩ)
Capacitor (10µF, 16V)
BC548 transistor
High resistance thermistor (NTC)
Diode (1N4001)
6V Buzzer
Working of fire alarm circuit
Working is based on the switching property of transistor.
The thermistor and R1 forms a potential divider network which drives the transistor.
The heart of this circuit is a thermistor. Thermistors are low-cost, easily-available temperature sensors widely used for uncomplicated temperature measurements.
Thermistors are temperature sensitive resistors. When temperature increases resistance offered by the thermistor decreases and vice versa. At normal temperature, the resistance of the thermistor is around 10kΩ.
All resistors vary with temperature, but the semiconductor materials used for thermistors are especially sensitive to temperature.
The transistor is turned ON by the voltage drop across the resistor R1.
Consider the temperature of the atmosphere is around 25°C, and then the resistance of thermistor is high so the voltage across the thermistor is also high according to the basic ohm’s law V=IR.
The threshold voltage can be set by varying the potentiometer (R1).
At this situation voltage across resistor R1 is low and it is not sufficient to turn on the transistor.
As temperature rises, the resistance of thermistor decreases so that the drop across the resistor R1 increases which turns ON the transistor.
When the transistor is turned ON, the current from Vcc starts to flow via 6V buzzer which produces a beep sound.
Diode is used for enabling unidirectional conduction and the capacitor removes sudden transients from the thermistor.



Yes i totally agreed with your blog post that professional security system is basic need for bank. It provides smart innovations in home and commercial security. I consider you to choose smart burglar alarm to protect your home measure and family safety from burglaries. It fills all of your security needs.
ReplyDelete